Daniel Cotton, Supriya Chakrabarti, Timothy Cook, Joshua Semeter, Valerie Taylor, et al.
Center for Space Physics
Boston University
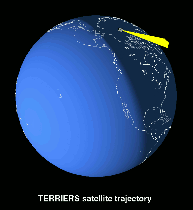
The Tomographic Experiment using Radiative Recombinative Ionospheric EUV and Radio Sources (TERRIERS) satellite is a small satellite designed to view and measure the upper atmosphere of the Earth. The satellite orbits the Earth at an altitude of 550 kilometers and continually spins end over end in a cartwheel configuration in the orbital plane. Data along the orbital plane is constantly collected via spectrographs aboard the satellite.
The collected data represents line-of-sight measurements of the Earth’s upper atmospheric densities all along the satellite’s orbit. The data therefore represents a Radon Transform of the actual atmospheric densities. In order to recover the original densities, the data is inverted using an iterative tomographic technique similar to those used in medical imaging Computer Aided Tomography (CAT) or Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scans. The algorithm used for this is a maximum entropy algebraic reconstruction technique developed by Josh Semeter, a graduate student at Boston University. With the inverted data representing the Earth’s actual upper atmospheric densities, scientists will study the dynamics and energetics of the upper atmosphere to understand more of the “weather” of the ionosphere and thermosphere.
Video Sequences

Video Sequence 1
TERRIERS Satellite Trajectory
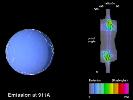
Video Sequence 2
Emission at 911A
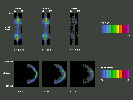
Video Sequence 3
Reconstruction of Volume Production at 911A – 35 iterations

Video Sequence 4
Reconstruction of Volume Production at 911A – 61 iterations
Still Images


Hardware: Graphics produced on a Silicon Graphics Onyx.
Software: Visualization done using IDL and graphics software written in C and OpenGL.
Graphics programming and video production: Erik Brisson, Scientific Computing and Visualization Group, Boston University.
Acknowledgments: This project was funded by the University Space Research Association and is a collaboration between Boston University, AeroAstro, the Massachusetts Institute of Technology’s Haystack Observatory, the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign and the Naval Research Laboratory.
