fNIRS noise regression with a multimodal extension of the General Linear Model using temporally embedded Canonical Correlation Analysis
Key Researchers: Alexander von Lühmann, BU; Meryem Ayşe Yücel, BU; David Boas, BU
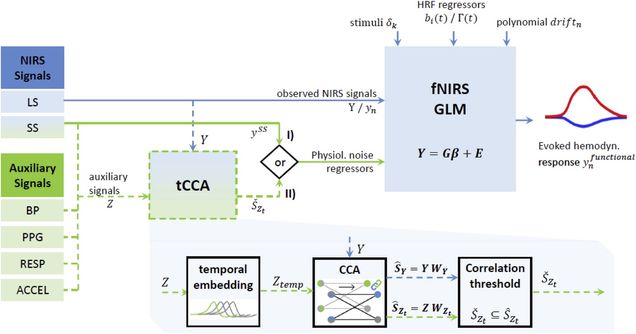
Summary: For the robust estimation of evoked brain activity from functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy (fNIRS) signals, it is crucial to reduce nuisance signals from systemic physiology and motion. Several challenging signal characteristics such as non-instantaneous and non-constant coupling are not yet addressed by conventional General Linear Model. In this work, we incorporate the advantages of regularized temporally embedded Canonical Correlation Analysis (tCCA) into the supervised GLM. This approach allows flexible integration of any number of auxiliary modalities and signals. We provide guidance for the selection of optimal parameters and auxiliary signals for the proposed GLM extension. GLM with tCCA significantly improves upon the current best practice, yielding significantly better results across all applied metrics: Correlation (HbOmax. +45%), Root Mean Squared Error (HbO max. -55%), F-Score (HbO up to 3.25-fold) and p-value as well as power spectral density of the noise floor.
Link: https://github.com/avolu/tCCA-GLM
Funding: This work was funded by a research contract under Facebook’s Sponsored Academic Research Agreement and in part by NIH R24NS104096