Laboratory Safety – Programs & Services
Please see below for information about the Laboratory Safety programs and services of most relevance to you.
Boston University has a robust animal care & use program including the Animal Science Center and the IACUC. Please see the Research Support site for information on animal care & use.
Guidance about the safe use and risks of biohazardous materials and organisms, including all infectious agents or biologically derived infectious materials that present either a risk or a potential risk to the health of humans or animals, either directly through infection or indirectly through damage to the environment.
Please also see:
- Biosafety Levels
- Boston University BPHC Permits
- Primary Containment
- Special Hazards
- Working with Biohazardous Materials
- Resources
Guidance about evaluating the risk(s) of chemicals in use, developing programs and procedures to ensure that they are used in a safe and healthful manner, and supporting compliance with all applicable federal, state, and municipal regulations
Please also see:
- The Chemical Hygiene Plan
- Chemical Inventories
- Chemical Safety Equipment
- Design and Engineering Controls
- Formaldehyde Toolkit
- Highly Hazardous Chemical Program
- Moving Chemicals & Hazardous Materials
- Medical Services and Surveillance
- Safe Handling and Storage of Chemicals
- Safe Work Practices
- Additional Resources & Information
Quick access to essential tools and information for Lab Safety Coordinators.
Please also see:
- Lab Safety Coordinators
- Roles and Responsibilities
- New Lab Personnel
- Lab Resources- Tools and Posters
- FAQ’s
Procedures to ensure that a space is free of contamination prior to the relocation or disposal of laboratory equipment, the re-certification or relocation of a laboratory, construction or renovations within a laboratory, or the vacating of a laboratory
Please also see:
- Laboratory Decontamination and Decommissioning: In Depth
- Equipment Decontamination Information for Contractors and Facilities Workers
Personal Protective Equipment, commonly known as “PPE”, is used to protect the body from chemical, biological, radiological, physical, electrical, mechanical, and other hazards that students, faculty or staff may encounter in an academic or professional environment. PPE appropriate to the task will be provided to BU faculty, staff, and students by their respective laboratories, departments, and/or supervisors. For additional information, refer to the resources tab at the bottom of the page or feel free to contact EHS at oehs@bu.edu.
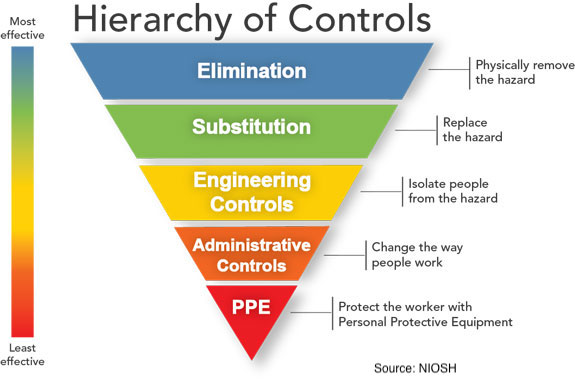
An important philosophy to remember is that PPE is the last line of defense. OSHA, NIOSH and BU EHS suggest following the Hierarchy of Controls illustrated below to provide the most effective protection for faculty, staff and students 1.
Assessment of Hazards
-
- Review the safety section of equipment and machinery manuals.
- Read Section 2 of the chemical safety data sheets (SDSs) used in your lab or workplace.
- Read the door placard before entering a laboratory (see figure below).
- Look for signage in lab or around machinery (see figure below).
- Research patterns or incidents of near misses, injuries or illness that have occurred in your workplace with materials or equipment that you are using.
- Communicate with current and former colleagues that are familiar with your operation.
- Reach out to EHS to perform a procedural risk assessment.

Once hazards have been identified, you, in collaboration with your colleagues, supervisor, and EHS, can identify PPE that will most adequately protect you. There are many types of PPE which can be used to protect from various maladies or routes of entry. Each type of PPE may have different makes or models, each with their own limitations such as service life or assigned protection factors (APF). APF helps determine if PPE will protect you based on the frequency, duration of work, and concentration of materials.
Examples of PPE:

For more information about respiratory protection visit this EHS Respiratory Protection Page.
Donning and Doffing
Donning |
Doffing |
1. First layer of gloves (if double gloving)* |
1. First layer of gloves (if you are double gloved)* |
2. Gown or lab coat |
2. Lab goggles or safety glasses |
3. Face mask or respirator (if any) |
3. Gown or lab coat |
4. Lab goggles or safety glasses |
4. Face mask or respirator (if any) |
5. Last layer of gloves (if double gloving) |
5. Last layer of gloves |
| *If double gloving is not part of your procedure, skip this step | |
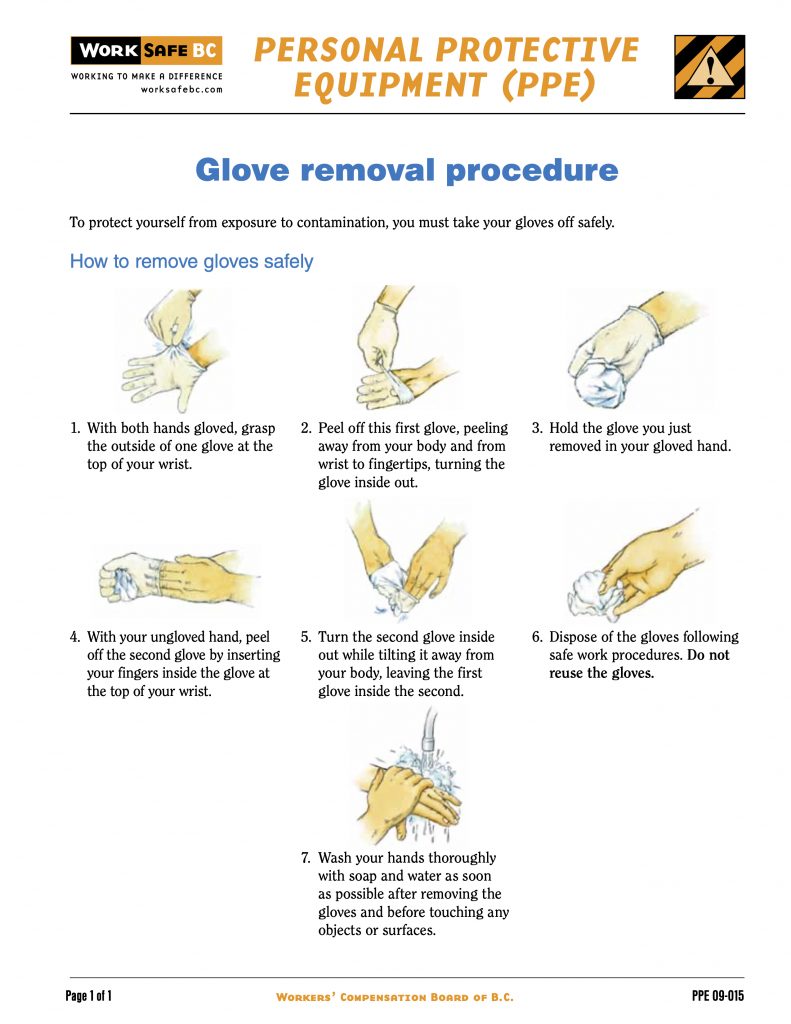
When doffing disposable gloves, it is important to follow a specific technique to reduce probability of transferring hazardous materials to your bare hands. See the diagram below for guidance 4.
Use and Maintenance of PPE
-
- Disposable gloves are SINGLE USE ONLY. Furthermore, if gloves break during your work, doff them correctly (see section above), wash your hands and don a new pair.
- Remove disposable gloves before reaching for commonly touched items. Items such as elevator buttons, stair railings and door handles should not be touched with a gloved hand. Always doff disposable gloves before exiting the laboratory.
- Do not wash body PPE with street clothing. Residual materials may stay on your street clothes when laundered with your body PPE. This could inadvertently expose your family and friends.
- If you can avoid it, do not bring PPE home. By keeping your PPE at work, you will reduce the likelihood of exposing your family and friends to dangerous materials.
- Always have spare PPE ready to use. Broken safety glasses or torn gloves are equivalent to not wearing protection at all. Never hesitate to throw out damaged or soiled PPE and get a new set.
- Inspect PPE for broken parts, rips, or holes. It can be hard to see damaged PPE during donning. Make sure you inspect your PPE one time before you enter a contaminated space or begin work.
- Make sure PPE is the correct fit. Similar to broken PPE, if the sleeves of your lab coat are too short or your nitrile gloves are too big, for example, your skin may be exposed, making you more susceptible to injury or illness.
- Store PPE in an area that will preserve it in good condition. Read the manufacturer instructions on how to store PPE. Keeping disposable gloves in a hot car or windowsill instead of a cabinet, for example, will degrade the nitrile/rubber and increase the likelihood of breakage during use.
Additional Resources
References
- “Hierarchy of Controls.” Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 13 Jan. 2015, https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/topics/hierarchy/default.html
- “Recommended Practices for Safety and Health Programs” Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 28 Sept. 2020, https://www.osha.gov/shpguidelines/hazard-prevention.html#ai1
- “Sequence for Donning and Doffing Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)” Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 28 Sept. 2020, https://www.cdc.gov/hai/pdfs/ppe/ppeposter148.pdf.
- “Glove Removal Procedure” WorkSafeBC, Workers Compensation Board of B.C., 24 November 2020, https://www.worksafebc.com/en/resources/health-safety/ppe-information-sheets/glove-removal-procedure?lang=en
This toolkit is meant to provide quick access to information, guidance and helpful tips for the use of Eyewash and Safety Showers.
Additional guidance documents:
Scientific Diving at BU includes scientific dives and snorkelers. <a href=”http://www.bu.edu/researchsupport/compliance/scientific-diving-safety/” target=”_blank” rel=”noopener noreferrer”>Please see the Research Support site for information on Scientific Diving</a>.<br />