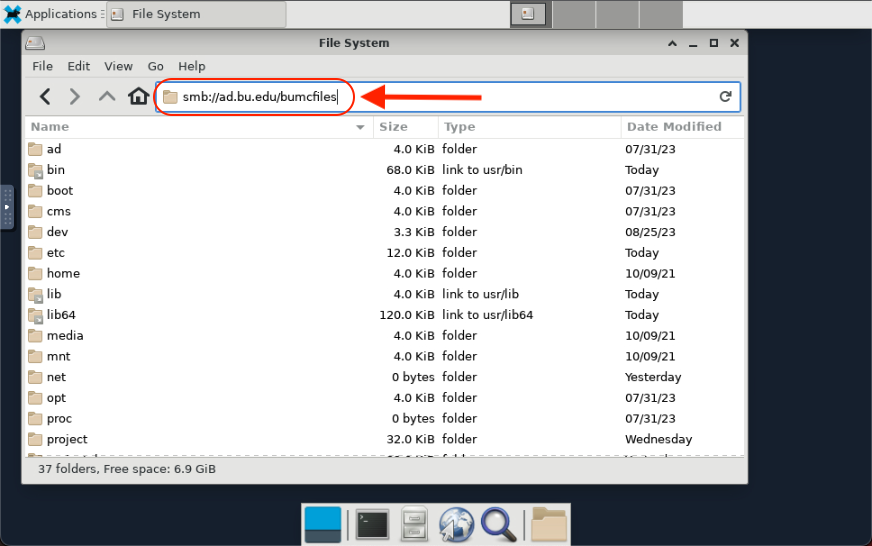
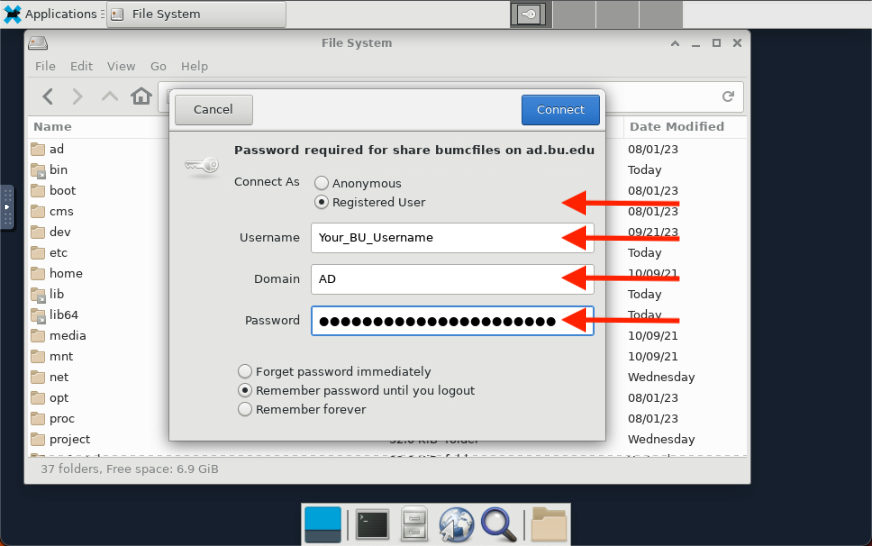
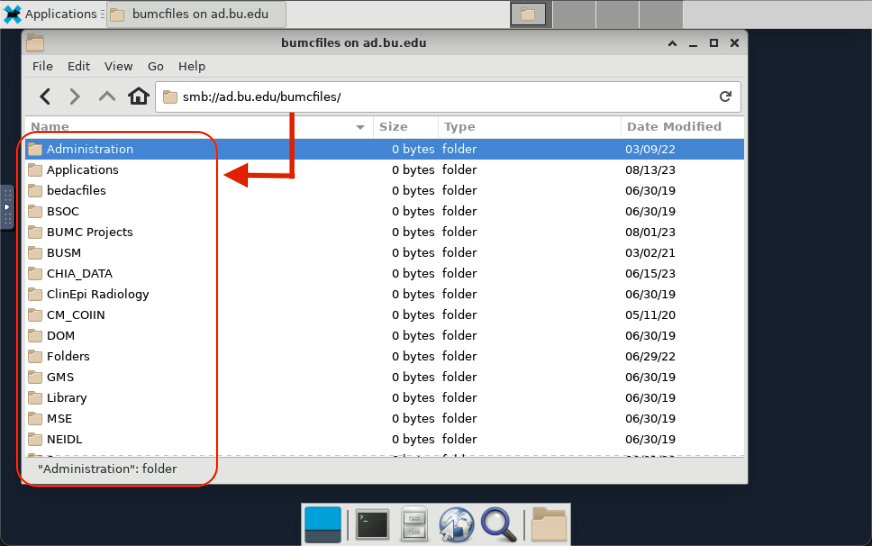
Researchers on the SCC can connect to remote file systems on the BU network for the purpose of transferring data. The steps to connect to these shares will depend on how the remote system exports the data share. Two common protocols and associated applications are described on this page.
- Windows SMB/CIFS Shares (e.g. IS&T NAS1, BUMC-IT Y-Drive)
- Network File System “NFS” Shares (e.g. Linux Systems, ENGNAS)
RCS recommends copying data from the remote file system to your SCC Project Space for faster data access in batch jobs.
Windows SMB/CIFS Shares
Windows SMB/CIFS shares on the BU network can be accessed from the SCC using either graphical file browsers or command line utilities. This is commonly used to connect to shares on the IS&T Network File Storage (nas1.bu.edu) and BUMC Y-Drive services, but the same approach may be applied to other remote data shares.
Using SCC OnDemand Interactive Desktop Session
Using smbclient from the Command Line
The smbclient utility provides directory navigation and file transfer for remote file systems using the SMB/CIFS protocol. Official documentation for smbclient can be found on the Samba website or directly from the SCC by typing man smbclient.
The example below demonstrates a connection to the BUMC Y-Drive.
- Connect to a remote share
scc1$ smbclient \\\\ad.bu.edu\\bumcfiles -W ad.bu.edu -U username
Enter AD.BU.EDU\username’s password:
Try "help" to get a list of possible commands.
smb: \>
- Navigate the share
Use the smbclient subcommands ls and cd to navigate the remote filesystem. Here we navigate to the SPH Environmental Health share and find myfile.txt. If the directory that you want to use has spaces, then the path should be put in quotes.
smb: \> cd SPH\EH\
smb: \SPH\EH\> ls
. D 0 Mon Feb 14 09:35:09 2022
.. D 0 Mon May 17 15:36:02 2021
myfile.txt F 1 Thu Jan 01 00:00:00 1970
- Transfer data
Use the smbclient subcommands get and put to transfer data to and from the SCC. The perspective for these sub-commands is from the SCC: a get copies the specified file from the remote share to the SCC directory and put will copy files from the SCC to the remote share. To transfer multiple files you can use the mget and mput commands.
smb: \> get "\SPH\EH\myfile.txt" "/projectnb/mySCCproject/myfile.txt"
getting file \SPH\EH\myfile.txt of size 18944 as /projectnb/mySCCproject/myfile.txt
- Close the connection
Use the exit command or Ctrl-D to close the connection. You will see the standard SCC prompt once the program exits.
smb: \> exit
scc1$
Network File System (“NFS”) Shares
Network File System (“NFS”) shares on the BU network can be accessed from the SCC using the automounter. The automounter utility is used to mount appropriately configured NFS shares from remote systems to the /net/ directory on the SCC so that data can be transferred to and from the SCC. This utility is always available on the SCC and a researcher need only navigate to the mount point to access the data. At BU, common NFS shares include IS&T Network File Storage, the ENGNAS and lab workstations.
Using the Automounter to connect to NFS shares
A researcher with access to a data share on
myremotesystem could do the following. In this example,
myremotesystem is the hostname or IP address of the remote file server. This directory will not appear in the
/net directory until it is accessed (e.g by using the
cd or
ls command) and the automounter mounts the share.
scc1$ ls /net/myremotesystem
Data stored on the IS&T Network File Storage service with NFS enabled can be accessed as follows. Note that not all IS&T Network File Storage shares are NFS enabled and you may need to use the SMB instructions in the section above.
scc1$ ls /net/nas1.bu.edu/proj/PROJECT_GROUP_NAME
Using the BU Engineering Share (ENGNAS)
The College of Engineering Information Technology department provides a network file storage system called ENGNAS to engineering research labs, courses, projects, student groups, and administrative units. The ENGNAS is accessible from the SCC via NFS as described in the previous section and is additionally linked to the path /ad/eng/ on the SCC for convenience. The /ad/eng/ path mirrors that of ENGNAS on ENG-Grid and on ENG-IT managed workstations to allow researchers to seamlessly move between computing environments using the same paths for scripts, data, and software. Additional information for the organization of this network share is detailed on the ENG-IT File Storage Knowledgebase.
The ENG-GRID file system is accessible through /ad/eng/:
scc1$ ls -l /ad/eng
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 25 Jun 10 2019 bin -> /net/engnas/eng_linux/bin
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 19 Jan 12 2020 courses -> /net/engnas/Courses
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 25 Jun 10 2019 etc -> /net/engnas/eng_linux/etc
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 25 Jun 10 2019 lib -> /net/engnas/eng_linux/lib
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 25 Jun 10 2019 opt -> /net/engnas/eng_linux/opt
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 25 Jun 10 2019 pkg -> /net/engnas/eng_linux/pkg
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 27 Jun 10 2019 pkg.7 -> /net/engnas/eng_linux/pkg.7
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 20 Jan 12 2020 projects -> /net/engnas/Projects
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 20 Jan 12 2020 research -> /net/engnas/Research
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 26 Jun 10 2019 sbin -> /net/engnas/eng_linux/sbin
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 17 Jan 12 2020 users -> /net/engnas/Users
NFS Configuration Notes
The following instructions are intended for system administrators of remote file servers that need to be accessed from the SCC. Research Computing staff are unable to directly assist with configuration of remote file servers.
Required Steps
- The remote filesystem must be on a BU network.
- Enable NFS on the remote system.
- NFS export the desired volume or directory on the remote system to the network ranges below.
192.12.187.128/26 — Login Nodes (scc1, scc2, geo) and public gateway to compute nodes.10.48.225.0/24 — SCC4, VirtualGL nodes, and private gateway to compute nodes.
Important considerations and notes
The remote filesystem should use BU usernames and group IDs, user accounts should have group membership matching that of the SCC, and the permissions of exported directories should be reviewed. Inconsistent IDs, group membership, and permissions can cause data access or exposure issues. If the user accounts on the remote file system are not BU compliant, then it may be needed to set squash on the export and map the user or group ids to something known on the SCC.