ExaFMM
ExaFMM is an open-source code base to utilize fast multipole algorithms, in parallel, and with GPU capability. The name reflects our viewpoint of the fast multipole method (FMM) as a rising star in the development of high-performance computing towards Exascale.Today (early-2012), the fastest supercomputers in the world have Petascale capacity, i.e., they are capable of performing in the order of 1015 floating point operations per second (flop/s). There are only a handful of scientific applications, however, that can sustain that performance. Even so, Exascale is already in the agenda, meaning applications need to be a thousand times faster and achieve 1018 flop/s.
The high-performance computing (HPC) community aims for the Exascale milestone to be reached by 2018. This forecast simply projects past performance evolution—but the challenges faced presently for evolving performance are unprecedented.
ExaFMM includes parallel, GPU-enabled, scalable algorithms for multipole-based “fast methods”, achieving O(N) complexity for the N-body problem. Originally, ExaFMM consisted of an FMM parallel code developed in the Barba group at Boston University. Later, it has grown to include other versions of FMM algorithms. See the Documentation section for more details. The codes are available freely for study, research, commercial or any use, under MIT License.
Please acknowledge its use in publications, cite the User’s Manual and/or our publications when appropriate, and give proper credit online.
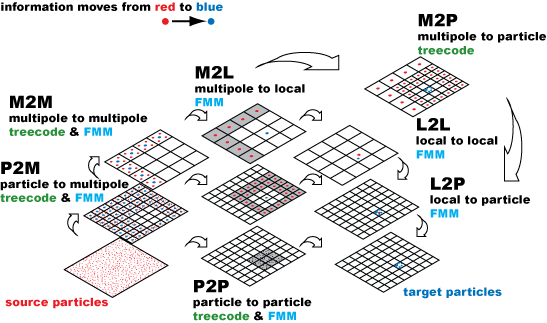
Copyrighted Image (top), appeared on: “Treecode and fast multipole method for N-body simulation with CUDA”, Rio Yokota, Lorena A Barba, Ch. 9 in GPU Computing Gems Emerald Edition, Wen-mei Hwu, ed.; Morgan Kaufmann/Elsevier (2011) pp. 113–132.