Nanotechnology solution to NAFLD – study reported in Nature Communications
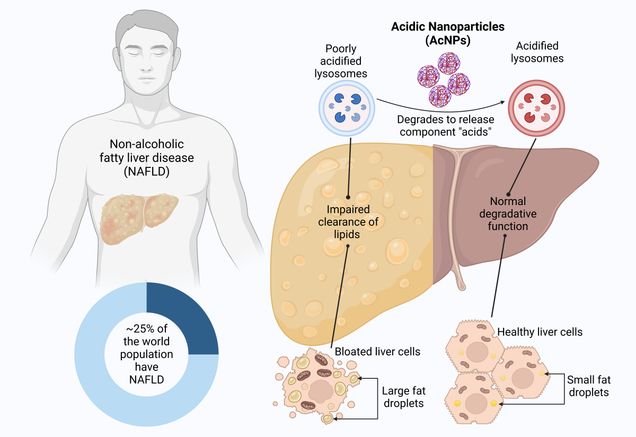
An international team of scientists led by BUnano Center Director Dr. Mark Grinstaff, Dr. Orian Shirihai (UCLA), and BUnano Crossdisciplinary Fellowship Alumna Dr. Jialiu Zeng (Nanyang Technological University, Singapore) reports on a new type of nanotechnology as a potential first-in-kind therapeutic for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), which affects 20 to 30% of the world’s population.
No current treatments target the liver directly to counteract the disease of excess fat droplets. In NAFLD, lysosomes – small organelles in liver cells – responsible for eliminating excess fat – do not function because of inadequate acidity. The study in Nature Communications, entitled “Restoration of Lysosomal Acidification Rescues Autophagy and Metabolic Dysfunction in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-38165-6)” investigates whether restoration of lysosomal function, by increasing its acidity, recovers liver performance and reduces the build-up of fat droplets. The team reports the synthesis of novel biodegradable acidifying nanoparticles as a lysosome targeting treatment. The acidifying nanoparticles, termed as AcNPs, composed of fluorinated polyesters, activate once in the lysosome, to increase the acidity to healthy levels and restore autophagic flux, mitochondrial function, and insulin sensitivity – all key physiological indicators of liver function. In established high fat diet mouse models of NAFLD, re-acidification of lysosomes via AcNPs treatment reverses fasting hyperglycemia and hepatic steatosis and returns liver function to lean, healthy levels.
Drs. Grinstaff and Zeng are excited about the ability to prepare new functional nanotechnologies which control cellular processes is exciting and opens new areas of research. Dr. Shirihai further states that this strategy also has significant clinical relevance and the potential to reverse the manifestations of obesity induced NAFLD and other metabolic disorders. This research started with initial funding from the BUnano Center as part of the faculty Pilot Grant project and was later continued by Dr. Jialiu Zeng as part of her BUnano Crossdisciplinary Fellowship research project.