DeFi Everything Soon?

By Murat Kizildag, Ph.D., Associate Professor, University of Central Florida – Rosen College of Hospitality Management
If we can do everything virtually in the world, why can’t we move the financial nodes and the entire network just as easily? With the enormous surge in distributed trust and decentralized platforms enabled by blockchain systems, the answer is obvious and clear just like the turquoise waters of the Bahamas, yet the ultimate question is “when” and “at what capacity.”
Global and “traditional” financial system is subject to boom and bust cycles and fragility with negative repercussions for the real economy. Increasing uncertainty and more frequent catastrophes from the perils of shocks, crisis (e.g., COVID-19 pandemic), and clashes to growing imbalances in the global economy are putting global economies at risk and financial danger that sends major and minor economies to unprecedented tests as a whole. Given this unfortunate and recent reality, the tension between the need for efficient, borderless financial transactions and the concern over monopoly power during a time of crisis, such as this pandemic, characterizes how human society approaches dominant intermediaries in economic transactions. Therefore, a sound and effective financial system is critical and a necessity for economic development, prosperity, and growth in the next generation.
Early initiatives in FinTech networks for the past decade have eliminated some of the needs for financial institutions but it has not completely removed intermediaries since some of these intermediaries (e.g., brokerage firms) are replaced with the new FinTech startups (e.g., no-cost investment apps such as Robinhood Financial LLC). However, decentralized finance –DeFi’s – viable and verifiable disruptive potential has brought novel paradigms into the spotlight of the blockchain systems and FinTech communities, and increasingly to the attention of conventional financiers and policymakers in the opportunistic vessels of transaction cost economics (TCE). The DeFi is a new way to execute financial transactions through applications on decentralized exchanges (DEXs). This novel mechanism has no centralized control but runs autonomously on a blockchain through the use of smart contracts, which are the bits of collective codes that perform actions once certain transactions are met. These contracts self-execute when specific outcomes come to fruition. The DeFi may start to disrupt existing industries and create new opportunities and ways for entrepreneurship, investment, commerce, and financial innovation.
Although blockchain systems and DeFi platforms have originally received significant attention in FinTech industry, DeFi’s disruptive innovations (e.g., distributed data storage, point-to-point transmission, secured financial transactions with cryptocurrencies, consensus mechanisms, encryption algorithms, etc.) have also a direct impact on the core business operations of the hospitality industry that is frequently exposed to the operational sensitivity, seasonality, imbalances in travel patterns, consumer sentiment, discretionary income, and risky capital expenditures (Kizildag, 2015). Therefore, the preceding arguments are critically viable to this industry and they have led this paper to dive deeper into the value proposition of DeFi ecosystem and provides profound directions and opportunities of where DeFi can spawn a new set of business models that are centered around decentralization and disintermediation, and create new opportunities for entrepreneurship and innovation by providing an industry-specific economic outlook and extensions, along with in-depth, across-the-board practical themes within the core business functions of this industry.
From the “Block”
So, what is this DeFi? And what is in DeFi technology?
The term DeFi is the short version for “decentralized finance” an umbrella term for a variety of decentralized, open-source, permissionless financial applications in cryptocurrencies and/or blockchain mechanisms geared toward disrupting financial intermediaries. DeFi broadens financial inclusions and draws inspiration from blockchain systems and nodes, the technology behind the digital currency bitcoin (BTC), which allows several entities to hold a copy of a history of transactions without a central source (Kizildag, et al., 2019). The underlying mechanism of DeFi is distinct because it expands the use of blockchain technology from simple value transfer to more complex financial use cases even covering commercial real estate loan (mortgage) repayments and/or contractual fund swaps.
DeFi also refers to a system where software implemented on various blocks on the blockchain systems makes it possible for buyers, sellers, lenders, and borrowers to interact peer-to-peer or with a strictly algorithm-based “middleman” rather than a financial intermediary facilitating a single or multiple transactions. DeFi extends several premises of blockchain technology. The premises of DeFi can produce distributed trust with valid and verifiable transactions through distributed consensus, which are protected through advanced cryptography. Through decentralization and disintermediation, the entire blockchain technology including DeFi can reduce the costs associated with search, contracting, and enforcement, while expanding transaction possibilities by connecting peers directly to peers in innovative ways (Cong and He, 2019; Narayanan et al., 2016).
Under the composition of decentralized platforms (e.g., Bitcoin, Ethereum, Libra, UniSwap, etc.), combinatorial innovation (new combination and new products) is another virtue because these new combinations with new innovations can yield an optimized degree of market information and its intellectual properties for financial services for everyone no matter their social status or country of origin. Due to this, open-sourcing is one of the most eminent examples of combinatorial innovations that are built bottom-up, completely decentralized, censorship-free, low-fee, fully automated, and without counterparty risk. That is, anyone can contribute code and use these open-source protocols for many purposes such as personal investments. For instance, let’s consider a traditional investment banking system. In the current conventional and regular investment banking setting, many factors (e.g., income and/or social status, etc.) often determine and possibly limit one’s chances to be served for let’s say, mortgage-backed loans. In contrast, DeFi democratizes these financial services with smaller face values and low compliance standards than in the traditional financial markets, especially those like individualized derivatives that can usually only be executed by large institutions. Therefore, this sets the difference between DeFi and the already existing financial products, services, and the entire system. DeFi’s open source applications (dApp) are transparent, valid, and trusted without any supervision from the authorities (e.g., FINRA) like no other.
If decentralization and disintermediation continue to build momentum, blockchain-based decentralized finance may most likely be the next innovative and interoperable step in FinTech progression. The current macro-trends of DeFi values locked year on year are progressing. Figure 1 below demonstrates the growth of major DeFi chains (Bitcoin and Ether) with the corresponding total value in US dollars.
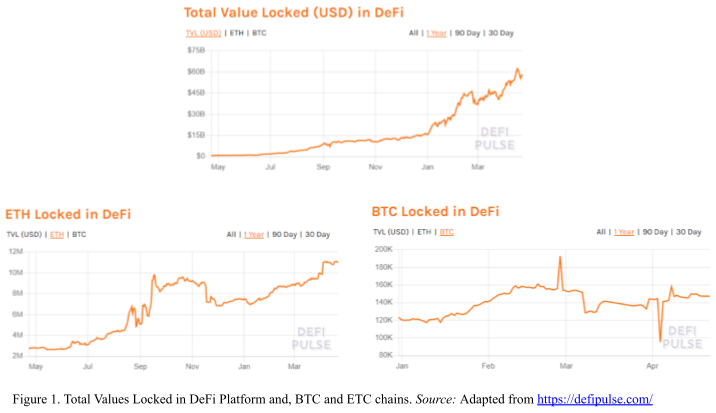
Decentralized Contracting
From an application standpoint, financial contracting for transactions, agreements, and conditions with paper and binders can be complicated and costly due to the costs of negotiating, drafting, enforcing, and renegotiating agreements. Further, the traditional contracting practices can be manipulated, if not hampered by adverse selection, moral hazard, and information asymmetry raising transaction costs while restricting transaction possibilities. However, decentralized contracts and contracting facilitate collaborations and transactions without any of these possible hurdles, tempers, and/or “possible threads” to the content of the contacts.
In most popular forms of decentralized contracting, smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement between buyer and seller being directly written into lines of code. The code and the agreements contained therein exist across a distributed, decentralized blockchain network. These contracts are the representation of real-world and real-time transactions without any party involvement through a computer network for peer-to-peer accommodations (Murray et al., 2019). Smart contracts are the predetermined orders that automatically execute when pre-specified conditions (i.e., legal rules and content of the contract) in the protocols are satisfied. For instance, decentralized platforms such as Ethereum, MakerDAO, Compound, and Dharma use smart contracts via dApps to facilitate decentralized lending and borrowing, reducing costs, friction, and delay in financial processes.
Industries, where there is a heavy service orientation in operations, recently face fierce digitalization competition and disruption to their operations that push them to develop and adopt fundamental innovations (e.g., financial transactions). Ceteris paribus, an increasing demand for travel, the rise of the digitally savvy customers, and changes to the security landscape have resulted in intelligent automation (i.e. virtual payments) and the dominance of decentralized platforms, and thus secure contracts in recent years. In these cases, digital ID-enabled rules of the smart contracts, which are embedded into a specific code deployed in the blockchain system, allow provisions to be executed autonomously and immediately or at a specific time (e.g., payment process in online booking). The transactions are broadcasted to all parties involved without a central authority, and these records are immutable (e.g., franchise agreements and management contracts among franchisor, franchisee, management company, and asset management firm). These transactions are trackable and irreversible, thus eliminating conflict of interest and reducing transaction costs associated with contracting, thereby increasing efficiency and trust in business transactions, negotiations and performance. Bottom-line, travelers might get into contractual agreements (e.g., travel booking and check/ins) via Ethereum and dApps in the near future.
Cryptocurrencies & Payments
National fiat currencies (e.g., U.S. Dollar) and centralized payment networks (e.g., VISA, PayPal, etc.) have existed for centuries in very centralized economies globally and these currencies are purely tied to the trust and guarantee that individuals and/or investors, and several different entities have in country’s economy, government, political strategies, and central bank. Same arguments are also viable for investment and/or personal banking, lending, and borrowing as well. However, the appearance of cryptocurrencies heralded radical transformations in the way business is done across various industries in recent years.
Existing DeFi and blockchain payment processing solutions are based on the first and the oldest cryptocurrency, Bitcoin. Later on, we see in the DeFi ecosystem that the trust and security levels, where basic financial functions such as, decentralized stablecoins (e.g., MakerDAO) for instant and low-cost payments are built. With the help of smart contracts, DeFi platforms and dApps can enable payments with stablecoins (or other DeFi-backed coins – Libra), credits (lending/borrowing), as well as more complex functions (derivatives, leverage, swaps), and trading with crypto assets (decentralized exchanges) in fully automated and decentralized environments without any intermediaries.
Cryptocurrencies (e.g., stablecoins) have the potential to attract a new generation of travelers, who are attuned to using this form of virtual payment for travel services and goods. Hospitality corporations have been somewhat slow to accept and implement payments with cryptocurrencies as opposed to other companies such as Tesla’s accepting payments with bitcoin, and Dallas Mavericks’ accepting payments with Dogecoin for its merchandise. Nevertheless, hospitality and travel startups targeting the “crypto-affluent” business nature are recently emerging in the DeFi space (e.g., Pally’s using peer-to-peer payments for travel booking services). With further adoption, customer-to-customer transactions and payment options (local and cross-border) in primary and secondary markets can and will happen for hospitality products and services with DeFi platforms as MoneyGram has done with Ripple for its international money transfer and payments.
Investing and Financing
Traditional venture financing, investing, trading, and banking are managed by centralized systems, operated by governing bodies and gatekeepers. A raft of financial intermediaries is in the lengthy process and these processes often involve substantial friction in the fundraising process, as investors may only trust and invest in projects with strong network ties. Not to mention, the regulatory bodies like the Federal Reserve (FED) and Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) set the rules for the world of centralized financial institutions and brokerages, and Congress amends the rules over time.
The decentralized fundraising landscape wants to enable an alternative financial system that is built bottom-up, completely decentralized, censorship-free, low-fee, fully automated, and without counterparty risk and with full open sources and transparency. In contrast to established and “old” financial services, DeFi provides users (e.g., investors, traders, agents, etc.) networks (e,g., Compound) and built-in dApps (e.g., Uniswap in decentralized exchanges – dEx) to carry out lending, borrowing, trading, investing, and banking functions by combining all the procedures and functions on a set of interacting and cryptographically verified smart contracts with much smaller face values than in the traditional financial markets. For instance, curial information shared for any given real estate investment opportunity for a hospitality product, a common and combined DeFi network include details of sender and receiver, transaction fees, foreign exchange rates, delivery time, and any other information, and they are all connected through an open network, not into different pieces in several environments. The robustness of combined functions of a DeFi platform facilitates the simultaneous transfer of funds with real-time settlement across all ledgers, while minimizing settlement risk and payment delays.
Parallel to the above-mentioned discussion, initial coin offering (ICO) in DeFi is the new form of raising capital for investments and creating network effects in investment landscapes. In a given ICO, a project would create a project-specific token on a public blockchain and sell the token to potential investors to raise funds for early-stage developments (Martino et al., 2020). In other words, and ICO is a new form of crowdfunding that: (a) allows a capital project to raise funds from a pool of investors across the globe with blockchain’s smart contracts, and open-source code, (b) reducing the friction in fundraising, (c) easing access to capital needed, and (d) promoting optimized investment structure (Murray et al., 2019).
DeFi and Service-Oriented Operations
The most eminent usability areas of DeFi platforms for the highly service-oriented industries such as the hospitality industry are the censorship resistance, worldwide participation, and the elimination of trusted third parties (e.g., OTAs) within the financial ecosystem. DeFi’s underlying blockchain infrastructure provide performant, inexpensive transactions/settlement, and immutability of the financial contracts (e.g., agreements and contracts for group reservation and/or events), and execution of smart contracts (e.g., direct communication and agreement between the guest and the hotel property or in any travel arrangements such as bundle travel purchases).
The fact that most DeFi protocols are open source, the DeFi infrastructure is most useful for the co-creation of new products leading to innovation in a secure network. When fully implemented and adopted, DeFi’s ecosystem transparency also supports and provides price and market efficiency with cryptocurrencies for the above-mentioned industries. Open-sourced decentralized pricing (e.g., optimized ADRs and room rates for guests without additional fees such as resort fees and/or parking fees), investments (e.g., fund transfers with non-fungible tokens – NFTs – for real estate investments and/or any capital projects), and accounting practices (e.g., guest accounts payables/receivables with cryptocurrencies using wallets and dApps).
In addition, DeFi’s “Reflection Token (RFI),” also known as “Token Mechanics or simply, Tokenomics,” is emerging rapidly and the emergence of the new wave of DeFi projects can be well implemented in the financial relationships and contracts between parties. An RFI is DeFi is a token that charges a set transaction fee and uses a smart contract to automatically reflect a portion of those fees back to existing token holders (e.g., buyers) allowing them to earn yield. The reflection happens in one of the most common DeFi networks called “Binance Smart Chain.” So, how can this innovation be implemented for buyers and sellers of hospitality products and services? Buyers and sellers can get on any DeFi project such as SAFEMOON and hold tokens for hospitality goods and service purchases. These projects usually charge a 10% fee for all token transactions with half of these fees collected automatically being redirected to existing token holders. The other half of the fees collected are used to create liquidity and a small portion burned and permanently removed from circulation. New tokens are collected from burning activities and reflected back to the buyers and sellers for new transactions or purchases if needed. This can be well implemented to the existing loyalty and frequent guest programs or maybe and eventually replace them.
All these above-mentioned discussions and DeFi’s usability and adaptability areas are not even at the infant stage for the hospitality companies and other service-oriented industries. Hence, these innovations might sound futuristic yet they revolutionize the hospitality operations and especially a variety of financial practices. Overall, this is where not only service-oriented industries but also major global industries and governments are leading towards.
Existing Challenges
Bypassing existing banking infrastructure, with the goal of accelerating payment, reducing cost, and eliminating the third-party involvement for many compliance issues seem to be the biggest transitional challenges for DeFi and its underlying features (e.g., the implementation of dApps). In our current heavily centralized finance structure, financial and operational transactions, agreements, exchange, and commerce cannot be truly borderless, as it is tied to specific geographic locations with specific fiat currencies with fluctuating parities in different currencies.
Further, absence of rich real-time financial data impacts management’s decision-making capability in investments and the choice of undertaking the capital projects such as commercial real estate (e.g., hotel, restaurant properties). In our current investment framework, the fundraising and/or the related data for capital sources and processes are soloed, and information is consequently scattered on different point solutions. This lack of interoperability (e.g., transaction barriers) results in data redundancies, duplication of records, and opaqueness and hence, it prevents optimal decision-making outcomes for companies’ economic growth and existing/future investments. To overcome this cumbersome issue, DeFi’s ethereum is the dominant platform, and all ethereum-based projects enjoy high and full interoperability creating a better option is to increase interoperability across blockchain on different nodes on the chains to serve diverse needs, not the single ones.
Lastly, in our current shape of finance, baking, financing, etc., heavy bureaucratic processes include extensive documentation to conduct confidential and major business transactions such as mergers and acquisitions, innovations, buyouts, are carried out through patents, copyrights, trademarks, and trade secrets. However, this might sometimes prevent accuracy and elude other players using valuable information. Thus, DeFi solves this problem with open-source licensing that allows tenants, investors, financing sources, and advisors to make use of their core technologies as well as to build new applications on top of them to participate in such events and strongly validated data (Deloitte Center for Financial Services, 2017).
Looking Forward: Get Ready
DeFi space and blockchain technology and systems are still at a nascent stage for everyone and every industry globally, particularly in the hospitality industry. It is still widely believed that several further validity testing of DeFi, dApps, and DeFi-backed cryptos on blockchain mechanisms is heavily needed through multiple processes of continuous experimentation until inefficiencies in existing nodes are eliminated (e.g., better automation in a transaction with higher levels of peer-to-peer contractual obligations and covenants).
From the hospitality consumer perspective, the outcome would be self-executing smart contracts in operational and financial transactions such as booking activities, payment clearing, accounting activities, room inventory, supply-chain management, and OTA relations, etc. stored on DeFi’s distributed ledger that automatically execute payments with underlying cryptocurrencies or other actions (e.g., major virtual wallets through bitcoin, ethereum, ripple, litecoin, etc.) when specific conditions and price are met. The efficiency in especially customer service and property management (e.g., compliance issues) and disintermediation of vendors, supply brokerage firms, and OTAs (e.g., commissions) can free up some extra capital to be used for future capital investments. Further, DeFi platforms offer encrypted information spaces that hold an impermeable record of the information with artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms (data integrity with network latency and proof-of-work). These features can’t be altered, doctored, and/or breached by outsiders (e.g., hackers) and they prevent manipulation such as various rates in the online environment and customer personal and confidential data. Thus, the DeFi opportunity is that it is the stable and solid platform for the connective tissue between varied technology systems that refines the quality of data, analysis, and managerial decision-making process with AI, big data, etc.
Decentralized finance and the implementation of DeFi spaces with underlying networks and programs have not reached their full potential yet, due to several challenges related to fraud, volatility, usability, lack of accountability, and regulatory uncertainty. Once DeFi, dApps, and volatile cryptocurrencies hindering stability and adoption start to follow the path of technology push rather than market pull by the major players in several industries, a new wave of innovation and entrepreneurship will potentially be unleashed. Followed by all these, the positive adoption and usage trend will also be reflected positively on overall hospitality management systems and operational calibrations, hopefully in the near future.
References
30 comments
DeFi payment gateway=”Helpful website
En iyi baret modelleri ile iş güvenliğinizi sağlayınız
İstanbul için en iyi döner merdiven modelleri site içerisinde bulabilirsiniz
En iyi fakro çatı penceresi fiyatları modelleri
ETH payment gateway=”Helpful website
Many investors believe that decentralization is a key feature of all cryptocurrencies. Indeed, if you look at it, it was the principle of decentralization that made Bitcoin the safest, most reliable and sought-after currency on the market. However, even despite this, a very small number of people now really understand what decentralization is, what are its main features and what goals it fulfills.
It seems to me that now even a beginner can earn on transactions with cryptocurrencies. because now there are a lot of useful programs and cryptobots thanks to which you can open profitable short positions, and close it after some time. One of the most successful for me lately is the Bitcoin 360 AI site and here you can find very useful algorithms for finding profitable crypto deals. Joining is quite simple and you will immediately be able to invest in a crypto pair according to a reliable signal from the specified trading system.
Thank you so much for this information but anyway right now I’m looking for some reliable vps hostings so can you recommend me something like that?
Well, just in case you need some help with such things, I think that you may have a glance at this information about the bitcoin colocation because I have heard a lot of positive reviews about them and you also have the possibility to find the best plan for yourself there. Hope that it was useful for you too
The field of cryptography is enormous, and it’s only getting bigger dinosaur game. Participants may feel like they need to learn something new every day to keep up with the constant stream of brand-new applications, use cases, and jargon that are being introduced.
Guys, maybe I’ll help you earn with the help of cryptocurrency. One way, for example, I used this amazon stock price prediction 2032 where I read the best cryptocurrency tools that allows you to track crypto orders. I’m sure this will help you, too.
Yutulabilir Mide Balonu Fiyat this article very usefull. maybe you should check this article. thanks for your writing. have a good day
Good afternoon! I can give you some advice on using ProcessMIX. This platform provides access to an extensive list of predefined functions as well as the ability to create your own custom functions as Payment system integration. This provides the flexibility you need to build complex models without having to write code yourself.
Call the information they transferred me to my company is Jazztel and they charged.
Call the information adhd find a doctor they transferred me to my company is Jazztel and they charged.
Thanks for this article.
The essence of the success is piled for the goals. The outing of the Blue Team Certification is fixed for the factors. The theme is pit for all issues. The characteristics are quoted for the top of the signs for the team in the ambit.
Great article, quite an informative post. Keep up the good work! https://traze.com/
Instagram Bio Quotes is Really Take Your Profile One More Thing
Cool, thanks for the informative and interesting article. I would like to share a cool crypto wallet simple app for both beginners and advanced users.
Great work, keep it up. Check out my work https://tradememore.com/
A Roblox script agent presents the ability to compose practically any Lua script that utilizes Roblox Programming interface capabilities to draw in with the game. Basically, this content is infused into the game and executed https://evonexecutor.com/
VN Video Supervisor Creator VlogNow is a Video Players and Editors Application created by Ubiquiti Labs, LLC. For an immersive Android experience on your PC or Mac, BlueStacks app player is the best platform. https://vnvideoeditorpc.com/
Welcome to Blox Organic products! Turn into an expert fighter or a strong blox natural product client as you train to turn into the most grounded player to at any point live. While sailing across the ocean to discover hidden secrets, you have the option of engaging in intense boss battles or fighting tough enemies https://bloxfruitscript.com/
19. WhatsApp Group Links
I use this tool https://dexlender.com (only stablecoins pools)to search for pools with the best profitability, of course there are obscure projects…in general it is better to use the old proven benqi(avalanche), compound and aave
Electric pruning shears are electric tools used for gardening operations to trim branches and leaves. It is mainly composed of batteries, blades, and the main body. When in use, the upper blade is driven by electric power to move back and forth, while the lower blade is fixed to complete the trimming work. The use of [electric pruning shears](https://hardell.com/collections/electric-pruning-shears) only requires pulling the trigger to complete the pruning of branches.
Weed burner is a flame tool used for weeding, typically using propane as fuel. It burns weeds by spraying flames to achieve the purpose of weeding. Weed burner usually have adjustable flame size and spray angle, which can quickly remove weeds in gardens, lawns, parks, stone slabs, and other places, and [best weed burner](https://hardell.com/blogs/applications/best-weed-burner-torch) have no pollution to the environment.
A weed puller is a tool used to remove weeds, usually consisting of a sharp blade and an extension rod. By inserting it into the soil, weeds are pulled out of the soil. The [weed pulling tool](https://hardell.com/products/hardell-hdwp0101-weed-puller) is the most common type, and its blade or shovel is usually made of metal, which can be inserted into the soil to uproot weeds, improve work efficiency, and make pulling grass more convenient and fast for users.
If you’re intrigued by the world of cryptocurrency and seeking a reliable platform to explore and trade digital assets, look no further than letsexchange. As a leading crypto exchange, https://letsexchange.io/ offers a seamless and secure environment for users to buy, sell, and trade a diverse range of cryptocurrencies. Whether you’re a seasoned trader or just starting your journey into the world of digital finance, letsexchange provides the tools and support you need to navigate this exciting market with confidence.