|
 |

PROJECTS
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Medical Robotics |
Optimal Port Placement for Minimally Invasive Surgery
A computer-based algorithm has been developed which uses preoperative images to provide a surgeon with a list of feasible port triplets ranked according to tool dexterity and endoscopic view quality at each surgical site involved in a procedure. A computer simulation allows the surgeon to select from among the proposed port locations. [Read More]
|
|
 |
|
|
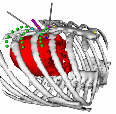
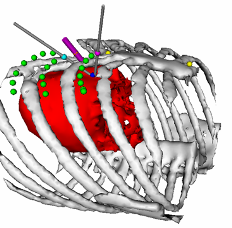
Optimal Port Placement for Minimally Invasive Surgery
A computer-based algorithm has been developed which uses preoperative images to provide a surgeon with a list of feasible port triplets ranked according to tool dexterity and endoscopic view quality at each surgical site involved in a procedure. A computer simulation allows the surgeon to select from among the proposed port locations. The procedure selected for the development of the system consists of a coronary artery bypass graft (CABG). In this procedure, the interior mammary artery (IMA) is mobilized from the interior chest wall, and one end is attached to the coronary arteries to provide a new blood supply for the heart. Approximately 10-20 cm is dissected free, using blunt dissection and a harmonic scalpel or electrocautery.
|
|
 |
|
References:
J. Cannon, J. Stoll, S. Selha, P. Dupont, R. D. Howe and D. Torchiana (2003). "Port Placement Planning in Robot-Assisted Coronary Artery Bypass," IEEE Transactions on Robotics and Automation, Vol. 19, No. 5, pp. 912-917.
J. Cannon, R. Howe, P. Dupont, J. Triedman, G. Marx and P. del Nido (2003). "Application of Robotics in Congenital Cardiac Surgery," Seminars in Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery: Pediatric Cardiac Surgery Annual, Vol. 6, No. 1, pp. 72-83.
[Reduce]
|
|
|
| Return to Top |
Robot Assisted Fetal Heart Surgery
It is sometimes possible and preferable to intervene early in the development of a fetus to correct congenital malformations. Topics of this research include developing image-based navigational interfaces and modeling tissue-instrument interaction forces for increased precision, reproducibility, safety, and speed of the surgical tasks. [Read More]
|
|
 |
|
|
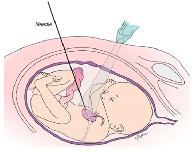
Robot Assisted Fetal Heart Surgery
It is sometimes possible and preferable to intervene early in the development of a fetus to correct congenital malformations. New transuterine minimally invasive procedures are being developed to correct such abnormalities in the 2nd and 3rd trimester of pregnancy. Topics of this research include developing image-based navigational interfaces and modeling tissue-instrument interaction forces for increased precision, reproducibility, safety, and speed of the surgical tasks.
|
|
 |
|
References:
M. Heverly, P. Dupont and J. Triedman (2005). "Trajectory Optimization for Dynamic Needle Insertion," Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics & Automation, Barcelona, pp. 1658-1663.
[Reduce]
|
|
|
| Return to Top |
Graphical Displays for Image Guided Surgery
The major obstacle facing surgeons learning to us lapUS is understanding how the ultrasound images are oriented relative to the patient. This project developed a system which provides orientation information by rendering the lapUS image plane relative to an aortagram in real time. [Read More]
|
|
  |
|
|
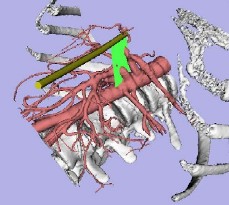
Graphical Displays for Image Guided Surgery
Over the past few years, several important applications for laparoscopic ultrasound (lapUS) have emerged, such as improved staging of hepatic and pancreatic malignancies. Despite these advances, surgeons have been slow to adopt lapUS. The major obstacle facing surgeons learning to use lapUS is understanding how the ultrasound images are oriented relative to the patient. The basis of this problem is that the orientation techniques used by transabdominal ultrasonographers are difficult to apply with laparoscopic instruments. This project developed a system which provides orientation information by rendering the lapUS image plane relative to an aortagram in real time. This display is helpful because it provides physicians with important spatial cues that ultimately improve their ability to interpret the ultrasound images. In the system validation trials, physicians identified more landmarks correctly using the navigation system (69% vs. 25%, p=0.02).
|
|
  |
|
References:
Suematsu Y, Martinez J. F., Wolf B. K., Marx G. R., Stoll J. A., DuPont P. E., Howe R. D., Triedman J.K., del Nido P.J. "Three-dimensional echo-guided beating heart surgery without cardiopulmonary bypass: atrial septal defect closure in a swine model." J. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2005 Nov;130(5):1348-57.
[Reduce]
|
|
|
| Return to Top |
Acoustic Diffuser for Use in Medical Instruments
Ultrasound images of medical instruments are blurred and unclear due to strong specular reflections from the metallic surfaces of the instruments, limiting the usefulness of ultrasound in applications where precision is necessary (e.g. surgery). The goal of our research is to reduce these specular reflections. [Read More]
|
|
 |
|
|
Acoustic Diffuser for Use in Medical Instruments
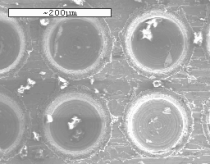
Ultrasound images of medical instruments include many imaging artifacts. One important cause of artifacts is the specularity of reflections from the metallic surfaces of the instruments, limiting the usefulness of ultrasound in applications where precision is necessary (e.g. surgery). The goal of this project was to reduce these specular reflections. The approach employed was to adapt the concept of an acoustic diffuser, first proposed by Manfred Schroeder in 1975 for concert halls, to an ultrasound application. Since manufacturing a diffuser which scatters high-frequency acoustic waves is expensive and impractical on a large scale, scattering properties of other surface geometries are also being investigated. The picture shows an acoustic diffuser, manufactured for investigative purposes at the Fraunhofer Center for Manufacturing Innovation at Boston University. This diffuser is an array of 34 x 34 "wells" drilled into an aluminum surface. Well depths are set such that sound is uniformly scattered in all directions. Each well is 100 microns in diameter.
|
|
 |
|
References:
Huang J, Dupont P, Undurti A, Triedman J, Cleveland R. "Producing Diffuse Ultrasound Reflections from Medical Instruments Using the Quadratic Residue Diffuser." Ultrasound in Medicine and Biology 2006;32(5):721727.
[Reduce]
|
|
|
| Return to Top |
|
CONTACT SENSING |
Modeling by Manipulation
At present, teleoperation is the only way that robots can perform sophisticated manipulation tasks in unstructured environments. We have been working to alleviate this situation by using information from the remote robot arm's sensors to assist in teleoperated manipulation tasks. [Read More]
|
|
 |
|
|
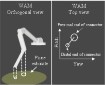
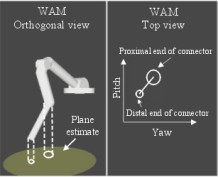
Modeling by Manipulation
At present, teleoperation is the only way that robots can perform sophisticated manipulation tasks in unstructured environments. In this control mode, the human operator performs all required sensing and planning, and generates all motion commands based on feedback from the remote environment. In practical teleoperation systems (e.g. undersea operations, tele-surgery, etc), the sensory feedback is often limited to video images without force feedback, which greatly restricts dexterity and productivity. We have been working to alleviate this situation by using information from the remote robot arm's sensors to assist in teleoperated manipulation tasks. We have derived algorithms that identify first order geometric properties such as dimensions and orientations.
|
|
 |
|
References:
Thomas J. Debus, Pierre E. Dupont and Robert D. Howe (2004).
"Multi-Channel Vibrotactile Display for Teleoperated Assembly," International Journal of Control, Automation and System, Vol.2, No. 3, pp. 390-397.
[Reduce]
|
|
|
| Return to Top |
Contact State Distingusihability and Identifiability
Autonomous manipulation tasks can be decomposed into sequences of contact states modeled by algebraic equations relating the parameters of the objects in contact with robot sensors. The goal of this research is to provide practical tools that can be used a priori to determine the global or local distinguishability and identifiability of contact states. [Read More]
|
|
 |
|
|
Contact State Distingusihability and Identifiability
Autonomous manipulation tasks can be decomposed into sequences of contact states modeled by algebraic equations relating the parameters of the objects in contact to the robot sensors. Success of task execution relies on the accurate estimation of the contact states. A rigorous approach to estimator design involves ensuring that the proposed set of sensors and associated contact state descriptions are sufficient (1) to distinguish each contact state, and (2) for each contact state, to identify the objects' physical parameters.
The goal of this research is to provide practical tools that can be used a priori to determine the global or local distinguishability and identifiability of contact states. [Reduce]
|
|
 |
|
|
| Return to Top |
STRUCTURAL DYNAMICS
|
Mechanical Realization
Before building main structures such as ship hulls and airplane fuselages on which equipments can survive, scaled mechanical models are often used to test structural design concepts. In this research, we want to study the design methods for mechanical emulators which preserve the driving-point behaviors of the active machineries (such as turbine generators, motors) and the passive equipments which are usually the most dynamically complex components in the dynamical system. [Read More]
|
|
 |
|
|
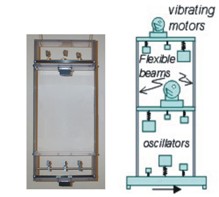
Mechanical Realization
Before building main structures such as ship hulls and airplane fuselages on which equipments can survive, scaled mechanical models are often used to test structural design concepts. In this research, we want to study the design methods for mechanical emulators which preserve the driving-point behaviors of the active machineries (such as turbine generators, motors) and the passive equipments which are usually the most dynamically complex components in the dynamical system. For the passive equipment emulators, the following approaches will be used. First, by using model reduction methods, reduced-order models will be achieved based on modal analysis data. Second, the reduced-order models will be realized by different approaches such as optimization procedure, electrical network synthesis and state space techniques. For active mechanical emulators, shakers will be used to emulate the active components in the machineries. [Reduce]
|
|
 |
|
|
| Return to Top |
MEMS Filter
High-Q Microelectromechanical (MEMS) resonators which are used for frequency selection can serve as on-chip replacements for off-chip crystal and SAW resonators. In this research, the concept of periodic structures has been used to design the MEMS resonators which have alternate stopbands and passbands. [Read More]
|
|
 |
|
|
MEMS Filter
High-Q Microelectromechanical (MEMS) resonators which are used for frequency selection can serve as on-chip replacements for off-chip crystal and SAW resonators. In this research, the concept of periodic structures has been used to design the MEMS resonators which have alternate stopbands and passbands. The dynamical responses of MEMS resonators are measured using Laser Doppler Vibrometer(LDV). Modal analysis and FEM techniques which have been widely used in macro mechanical structures are used to investigate dynamical properties of these MEMS resonators. [Reduce]
|
|
 |
|
|
| Return to Top |
TACTILE DISPLAY
|
Multichannel Vibrotactile Display
Overlaying visual displays with an endoscope view during surgery can be costly and non-intuitive due to scene complexity and the wide range of viewpoints encountered. Within this context, a multichannel vibrotactile device was designed, developed and tested for sensory substitution during teleoperation. [Read More]
|
|
 |
|
|
Multichannel Vibrotactile Display
Augmenting perception in man-machine systems consists of two parts. First, machine sensor data must be interpreted in a way appropriate to the task. Second, the task-specific information must be communicated to the operator in a format that addresses the limitations of human sensory information processing. For example, during teleoperated surgery, vocal communication between non-operator team members can interfere with an auditory display. Similarly, overlaying visual displays with an endoscope view during surgery can be costly and non-intuitive due to scene complexity and the wide range of viewpoints encountered. Within this context, a multichannel vibrotactile device was designed, developed and tested for sensory substitution during teleoperation.
|
|
 |
|
References:
Thomas Debus, Pierre Dupont, Tae-Jeong Jang, and Robert Howe (2002).
"Multichannel Vibrotactile Display for Teleoperated Assembly," Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics & Automation, Washington D.C, 11 May 2002.
[Reduce]
|
|
|
| Return to Top |
FRICTION ANALYSIS
|
Friction Modeling
There are three goals of this research. The first is to develop physically-based friction models for control and damping applications. The second is to derive techniques for on-line identification of friction parameters. The third is to derive control techniques which are robust with respect to variations in frictional dynamics. [Read More]
|
|
 |
|
|
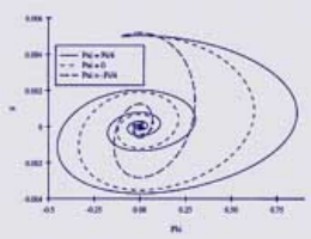
Friction Modeling
The nonlinear and dynamic behavior of friction is often a significant impediment to precision motion control in systems as diverse as disk drives and machine tools. There are three goals of this research. The first is to develop physically-based friction models for control and damping applications. The second is to derive techniques for on-line identification of friction parameters. The third goal is to derive control techniques which are robust with respect to variations in frictional dynamics. [Reduce]
|
|
 |
|
|
| Return to Top |
BIOMECHANICS
|
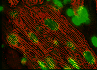
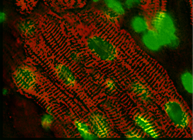
Atrial Biomechanics
Because of its location relative to the chest wall and the relative lack of motion (as compared to the other chambers of the heart) the Right Atrium (RA) is thought to be an optimal location for port entry in tele-robotic heart valve repair. This project is exploring the effect of port insertion and movement on tissue viability. [Read More]
|
|
 |
|
|
Atrial Biomechanics
Because of its location relative to the chest wall and the relative lack of motion (compared to the other chambers of the heart) the Right Atrium (RA) is an ideal location for transmural port entry for beating-heart intracardiac repair. While the RA is of minimal importance as a mechanical pump, the electrical signals which stimulate the contractions in the heart pass through the RA. This project explored the effect of port insertion and movement on tissue viability. Areas studied include fiber alignment, stress/strain relationships, and signal propagation. [Reduce]
|
|
 |
|
|
| Return to Top |
|
|
|
|


